10 SaaS Ops tips for IT leaders
If you’re unfamiliar with SaaS Ops and its potential to boost productivity, cut costs, and mitigate risks for your business, you’re in the right spot. Discover the obstacles and advantages of SaaS Ops, along with ten recommendations for IT executives seeking to elevate their SaaS Ops game.
What is SaaS Ops?
SaaS Ops, or SaaS operations management, is the process within an organization for the deployment, configuration, and ongoing management of SaaS, or software-as-a-service applications.
SaaS Ops aims to streamline the management of applications to improve security, increase efficiency, optimize spend, ensure compliance, and enhance the employee experience.
Why should businesses focus on SaaS Ops management?
Many businesses today are focused on digital transformation, cloud computing, and hybrid workplaces. These trends have led to an increase in the use of SaaS applications, as they offer the flexibility and scalability required to support these new ways of working.
SaaS applications can be deployed quickly, require minimal maintenance, and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote work and distributed teams.
But along with all of the benefits of SaaS applications, rapidly changing SaaS portfolios bring on a host of potential issues to manage. Businesses need a way to effectively manage their SaaS applications to ensure productivity, security, efficiency, cost optimization and more.
What are the benefits of SaaS Ops management
- Visibility and control
- Automated license provisioning
- Cost optimization
- Compliance tracking
SaaS Ops can provide numerous benefits to organizations that heavily rely on SaaS applications. The first is improved visibility and control. With SaaS Ops, you can get a clear picture of what applications are being used across the organization, who is using them, and how they are being used. This can help identify and manage shadow IT, enforce compliance and security policies, and lay the groundwork for optimizing SaaS spend.
SaaS Ops can enable you with automated license provisioning processes to quickly provide employees with access to the applications they need while also removing access to applications that employees no longer use.
This provides value in two ways. Firstly, employee productivity improves when they don’t have to wait around for days, or even weeks, for access to tools. And secondly, when an employee’s license is reclaimed, it can be redeployed to another employee without having to purchase an additional license. Diligent license reclamation can also help you avoid true ups.
Another key benefit is cost optimization. By cataloging applications and monitoring usage, you can understand which applications are redundant and underutilized and retire them. When contracts come up for renewal, you’ll have a better sense of how many licenses you actually need, so you’re not relying on what the vendor recommends.
SaaS Ops can also help you track and monitor the compliance of applications across your portfolio, so you can ensure you’re investing in applications you can trust. It can also help you identify applications that can be moved behind SSO to improve security.

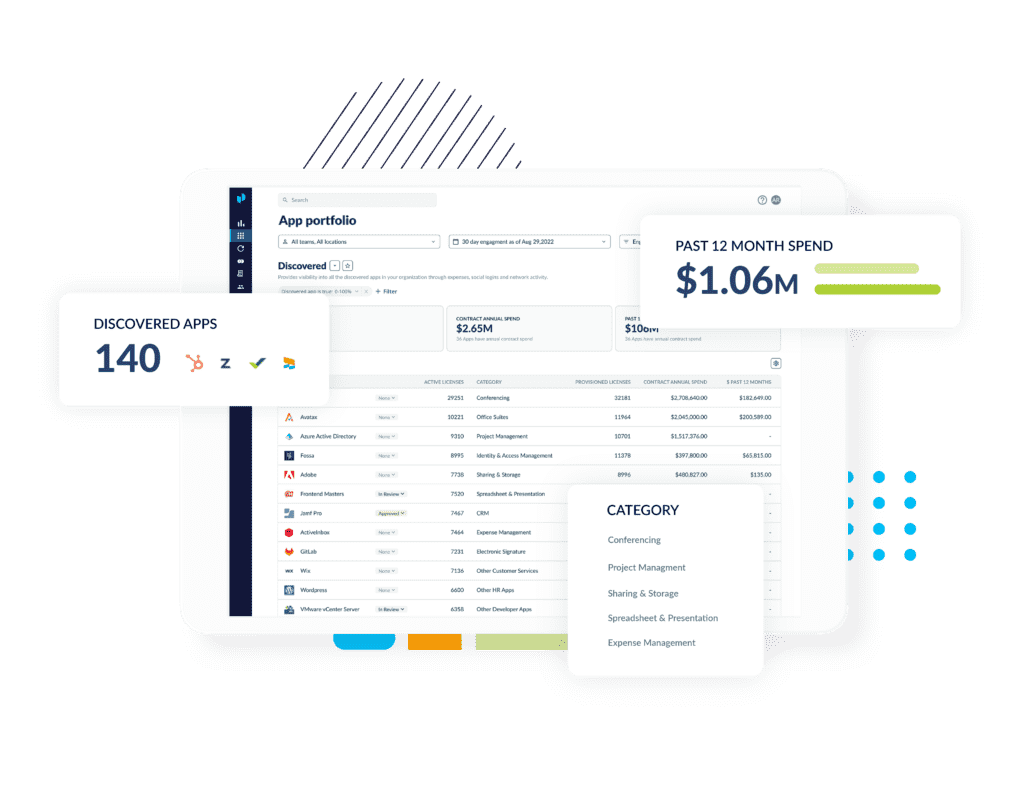
What does a SaaS Management Platform look like?
Who is on a SaaS Ops team?
A fully developed SaaS Ops team contains many different roles. Depending on the size of the organization, one person often takes on multiple roles. Additionally, organizations often focus their efforts around a few key areas of SaaS Ops that are most important to them. As such, they may not have teams that support all aspects of SaaS operations management.
Here are some of the roles on a SaaS Ops team and what they do:
- SaaS Operations Manager: oversees the entire SaaS Ops team, responsible for setting strategy and ensuring effective operations of SaaS applications.
- SaaS Operations Architect: responsible for designing the infrastructure and architecture of SaaS applications to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
- SaaS Operations Engineer: responsible for the implementation and management of SaaS applications and the underlying infrastructure.
- SaaS Security Analyst: responsible for ensuring the security and compliance of SaaS applications, as well as monitoring for any potential security threats or breaches.
- SaaS Compliance Officer: responsible for ensuring that the organization is meeting any regulatory or compliance requirements related to the use of SaaS applications.
- SaaS Application Administrator: responsible for the day-to-day administration and support of specific SaaS applications.
- SaaS Data Analyst: responsible for analyzing and reporting on data from SaaS applications to support business decisions.
- SaaS Integration Specialist: responsible for integrating SaaS applications with other systems and applications used within the organization.
- SaaS Vendor Manager: responsible for managing relationships with SaaS vendors and ensuring that service level agreements (SLAs) are being met.
- SaaS Training Specialist: responsible for training employees on how to effectively use SaaS applications and maximizing their potential.
What department these roles sit under also varies from company to company. And sometimes the roles will be split between departments. For example:
- IT: SaaS Ops teams may be part of the IT department and work closely with other IT teams such as infrastructure, networking, and security.
- Operations: SaaS Ops teams may be part of the operations department and work closely with teams responsible for business operations, such as finance, human resources, and customer support.
- Digital transformation: Some organizations have a separate department dedicated to digital transformation, which includes SaaS Ops as a critical function.
- Product: In some cases, SaaS Ops teams may report to the product department, especially if the SaaS applications are used by the organization’s products or services.
- Security: SaaS Ops teams may be part of the security department, especially if the focus is on ensuring compliance and protecting data.
The key is to first understand what your critical goals are for SaaS Ops, then identifying which roles you need to build out to effectively achieve those goals. Once you identify your goals and roles, the department under which you build out the team should become clear.
What are the key components of SaaS Ops management?
SaaS Ops involves a number of key components that work together to help businesses manage their SaaS applications more effectively. These include:
- Application discovery and inventory: Identifying and cataloging all SaaS applications used across the organization.
- User access and authorization: Managing user access to SaaS applications, enforcing security policies, and monitoring user activity.
- Performance monitoring and management: Monitoring the performance and availability of SaaS applications, identifying and resolving issues, and optimizing application performance.
- Spend management: Tracking SaaS spending, identifying opportunities to reduce costs, and optimizing SaaS contracts and subscriptions.
- Automation and workflows: Automating SaaS management tasks, streamlining onboarding and offboarding processes, and enforcing compliance policies.
What are the challenges of SaaS Ops management?
Implementing SaaS Ops has many benefits, but it can be hard to do without the right tools. Some of the challenges you’re likely to face include:
- Complexity: Managing a large number of SaaS applications across different departments and teams can be complex and time-consuming, especially if businesses don’t have the right tools and processes in place.
- Security risks: The use of shadow IT and rogue SaaS applications can increase the risk of data breaches, cyber attacks, and other security threats.
- Lack of visibility: Without proper SaaS Management tools, businesses may lack visibility into their SaaS spending, user activity, and application performance.
- Integration issues: Integrating SaaS applications with other enterprise systems and applications can be challenging, especially if there are compatibility issues or data silos.
- Changing landscape: The SaaS landscape is constantly evolving, with new applications and vendors entering the market all the time. Staying on top of these changes and managing SaaS applications effectively can be a challenge.
To address these challenges, you should consider implementing best practices such as regular SaaS application audits, leveraging SaaS Management Platforms, using security and compliance frameworks, and establishing clear policies and procedures for SaaS usage. Taking proactive steps to manage your applications effectively can go a long way to help mitigate risks associated with SaaS-forward companies and ensure you’re getting the most value from your investments.
10 SaaS Ops tips for IT leaders
- Prioritize SaaS application visibility: To effectively manage SaaS applications, IT leaders must have a clear understanding of what applications are in use across the organization. We found that the average organization uses 342 SaaS applications, 48% of which are shadow IT.
- Manage user access and permissions: It’s important to ensure that users have access only to the applications they need to perform their job functions. We also found that 55% of SaaS licenses go unused every year, due in part to applications being widely provisioned.
- Focus on cost control: SaaS applications can be expensive, so it’s important to track costs and optimize spending wherever possible.
- Ensure compliance: With an ever-increasing number of regulations and policies to comply with, it’s essential to have processes in place to ensure compliance with all relevant requirements.
- Continuously monitor and optimize application performance: Regularly monitoring application performance can help identify and resolve issues before they become major problems.
- Use automation where possible: Automating routine tasks can help reduce the workload for IT teams and improve efficiency. Some companies can spend 2,000-4,000 hours annually manually collecting data from each app and then removing or changing licenses assigned to employees. The number of license events can reach into the millions.
- Prioritize employee education: Ensuring that employees are properly trained on SaaS applications and best practices can help improve security and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Foster collaboration between IT and business teams: Effective SaaS Ops management requires collaboration between IT and business teams, so it’s important to foster a culture of collaboration.
- Stay up-to-date on SaaS trends and best practices: SaaS technology is constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices to ensure that the organization is making the most of its SaaS applications.
- Invest in a SaaS Management Platform: Effectively managing a large SaaS portfolio with a small team is nearly impossible without the visibility, insights, and automation provided by an SMP.
About Productiv:
Productiv is the IT operating system to manage your entire SaaS and AI ecosystem. It centralizes visibility into your tech stack, so CIOs and IT leaders can confidently set strategy, optimize renewals, and empower employees.